i_need_contribute
i_need_contribute
Yu Wang a 1, Liangzhen Xie b, Fangyuan Liu b, Danni Ding a, Wei Wei a, Fengjuan Han b
a
Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine, Harbin, 150040, China
b
Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine, Harbin, 150040, China
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2023.117299
As a "silent killer" that threatens women's lives and health, ovarian cancer (OC) has the clinical characteristics of being difficult to detect, difficult to treat, and high recurrence. Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) can be utilized as a long-term complementary and alternative therapy since it has shown benefits in alleviating clinical symptoms of OC, decreasing toxic side effects of radiation and chemotherapy, as well as enhancing patients' quality of life.
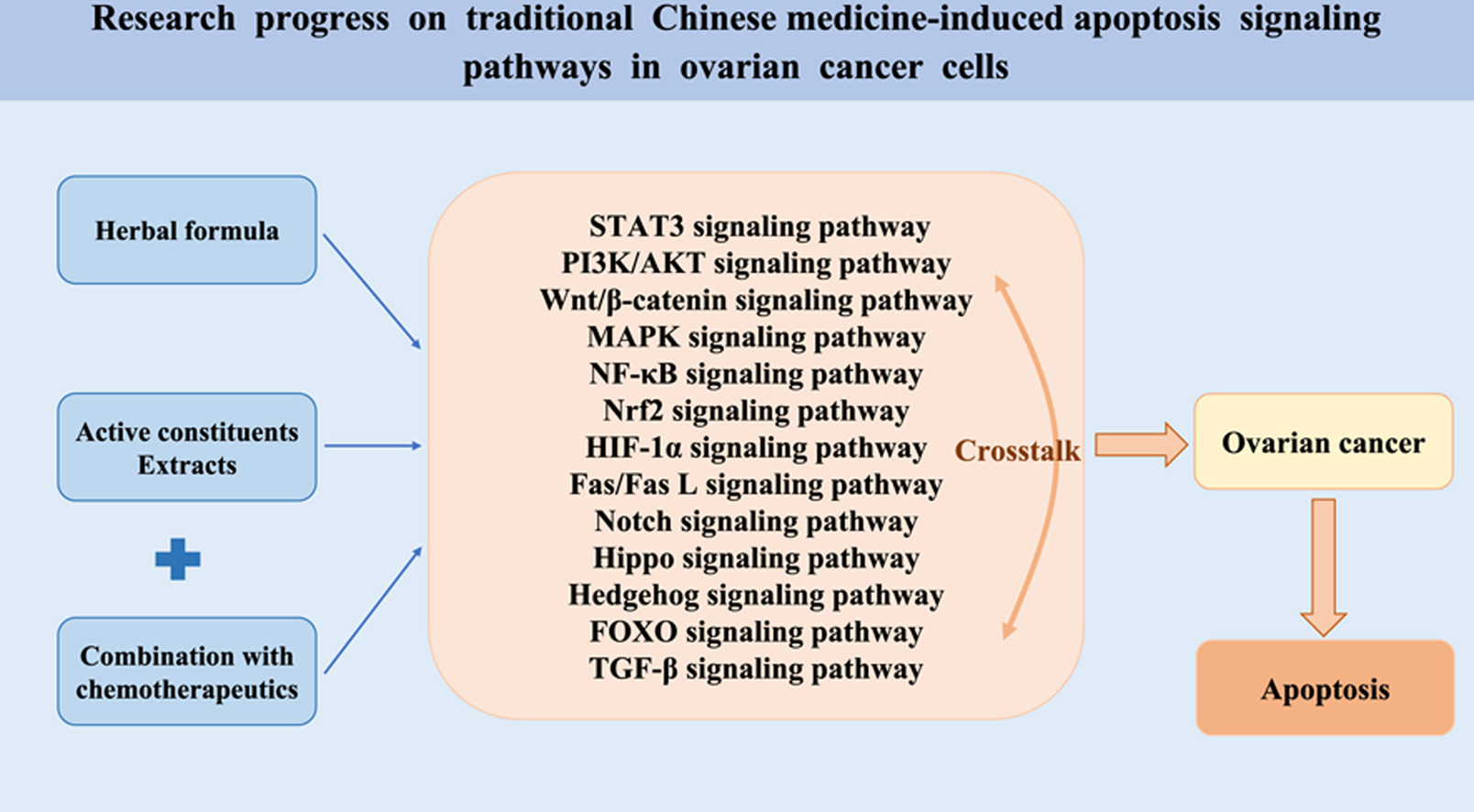
This paper reviews how TCM contributes to the apoptosis of OC cells through signaling pathways, including active constituents, extracts, and herbal formulas, with the aim of providing a basis for the development and clinical application of therapeutic strategies for TCM in OC.
The search was conducted from scientific databases PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, CNKI, Wanfang, VIP, and SinoMed databases aiming to elucidate the apoptosis signaling pathways in OC cells by TCM. The articles were searched by the keywords "ovarian cancer", "apoptosis", "signaling pathway", "traditional Chinese medicine", "Chinese herbal monomer", "Chinese herbal extract", and "herbal formula". The search was conducted from January 2013 to June 2023. A total of 97 potentially relevant articles were included, including 93 articles on Chinese medicine active constituents or extracts and 4 articles on Chinese herbal compound prescriptions.
TCM can induce apoptosis in OC cells by regulating signaling pathways with obvious advantages, including STAT3, PI3K/AKT, Wnt/β-catenin, MAPK, NF-κB, Nrf2, HIF-1α, Fas/Fas L signaling pathway, etc.
Chinese medicine can induce apoptosis in OC cells through multiple pathways, targets, and routes. TCM has special advantages for treating OC, providing more reasonable evidence for the research and development of new apoptosis inducers.